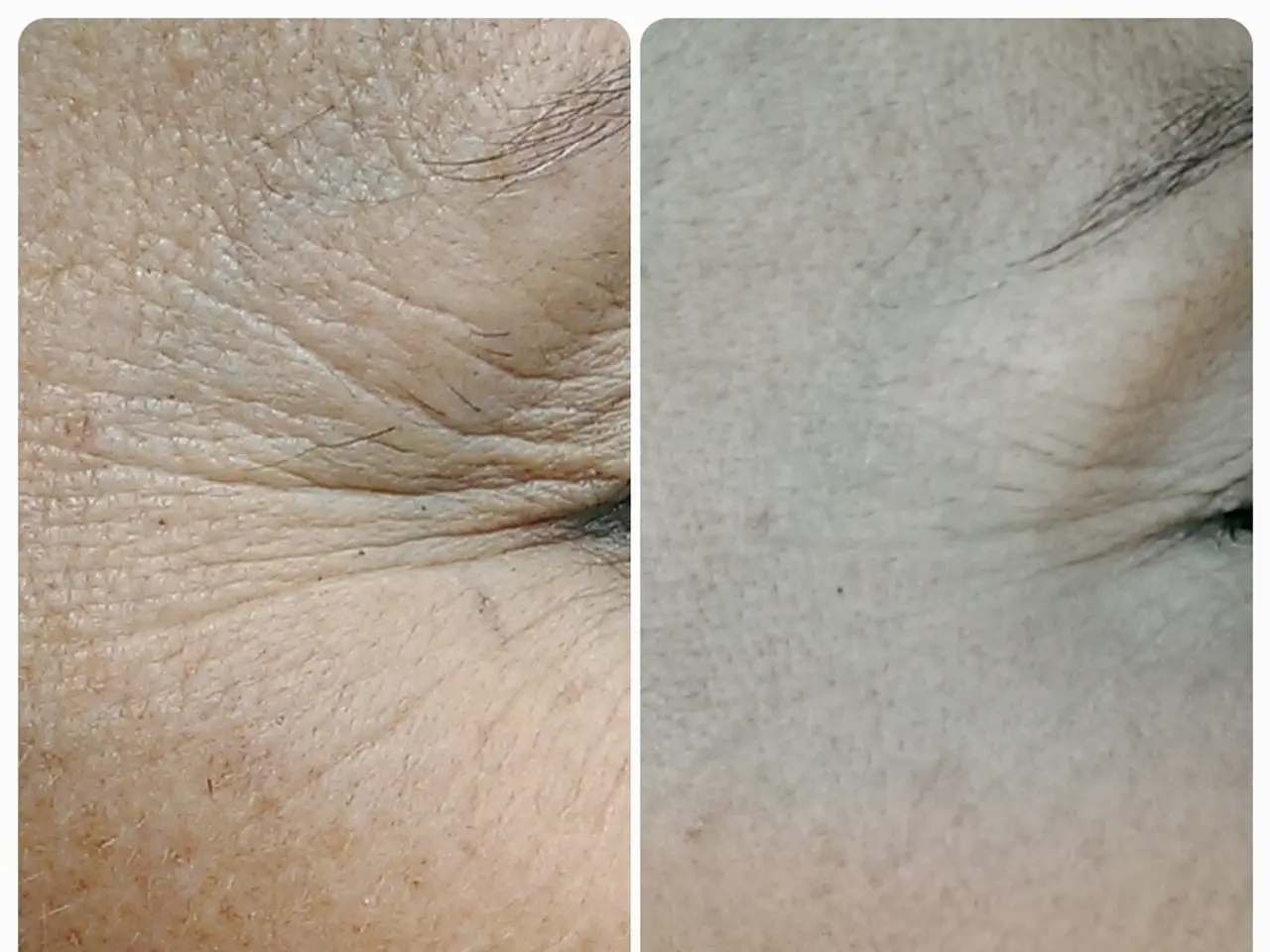
Enhanced Medical Gadget Boosts Healing Speeds by an Impressive 30 Percent
In a groundbreaking development, UK scientists have created a portable, non-invasive medical device that could potentially speed up wound healing by up to 30%. This innovative device, which has shown significant improvements in lab tests, leverages the well-understood technology of ultrasound to reawaken the natural abilities of skin cells.
The device works by delivering controlled mechanical energy through focused ultrasound waves, stimulating skin cells surrounding a wound. This, in turn, activates cellular mechanotransduction pathways, influencing critical processes like cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, promoting tissue regeneration and repair without thermal damage.
The technology could be particularly beneficial for those who struggle with chronic wounds, such as diabetics and older adults. Diabetic foot ulcers, for instance, affect more than 25% of people with diabetes during their lifetime and are a leading cause of lower limb amputations. By potentially reducing healing times dramatically, this device could help mitigate these devastating consequences.
The device has already passed crucial proof-of-concept hurdles, having been tested on human skin cell cultures and animal models. It's designed for use outside hospitals, which could lead to fewer surgeries, less antibiotic use, shorter hospital stays, and a better quality of life for millions of people.
However, despite these promising results, the device is still undergoing preclinical and clinical research. The next steps include rigorous human trials, device optimization, and regulatory approval by agencies like the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the UK's Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).
The hurdles for regulatory approval could be lower than for a brand-new drug, given that ultrasound technology is already in use. This could potentially shorten the development timeline, with the technology potentially available in clinics in as little as three to four years, assuming further trials confirm its safety and effectiveness.
If the device proves as effective as early tests suggest, there's a future where ultrasound healing technology could be accessible at home. This could save the UK's National Health Service up to £3.1 billion annually, a significant boost for healthcare budgets.
The cells respond to the device by allowing a calcium surge, which acts like a wake-up call, telling the cells to get moving. This stimulation accelerates the healing process, making the cells behave as if they're decades younger. The team is currently focusing on fine-tuning the ultrasound frequency and duration for maximum effectiveness.
In summary, this innovative device holds great promise for the future of wound healing. By harnessing the power of ultrasound technology, it promises to accelerate wound healing through mechanoregulatory activation of cellular pathways, promoting tissue regeneration without thermal damage. With further research, clinical trials, and regulatory approval, this device could revolutionise the treatment of chronic wounds, improving the quality of life for millions and potentially saving billions in healthcare costs.
- This innovative device, utilizing the technology of ultrasound, could revolutionize the treatment of medical-conditions such as chronic wounds by speeding up healing rates by up to 30%.
- The technology of this device, currently being tested, is shown to influence critical processes like cell proliferation and differentiation in health-and-wellness, particularly beneficial for those with conditions like diabetic foot ulcers.
- In fitness-and-exercise and skin-care, the technology behind this device may one day be accessible at home, potentially saving healthcare costs and improving lifestyles.
- To make this device more effective, therapies-and-treatments like fine-tuning the ultrasound frequency and duration are being focused on by the research team.