Infant Acid Reflux: Understanding Causes, Signs, and Remedies
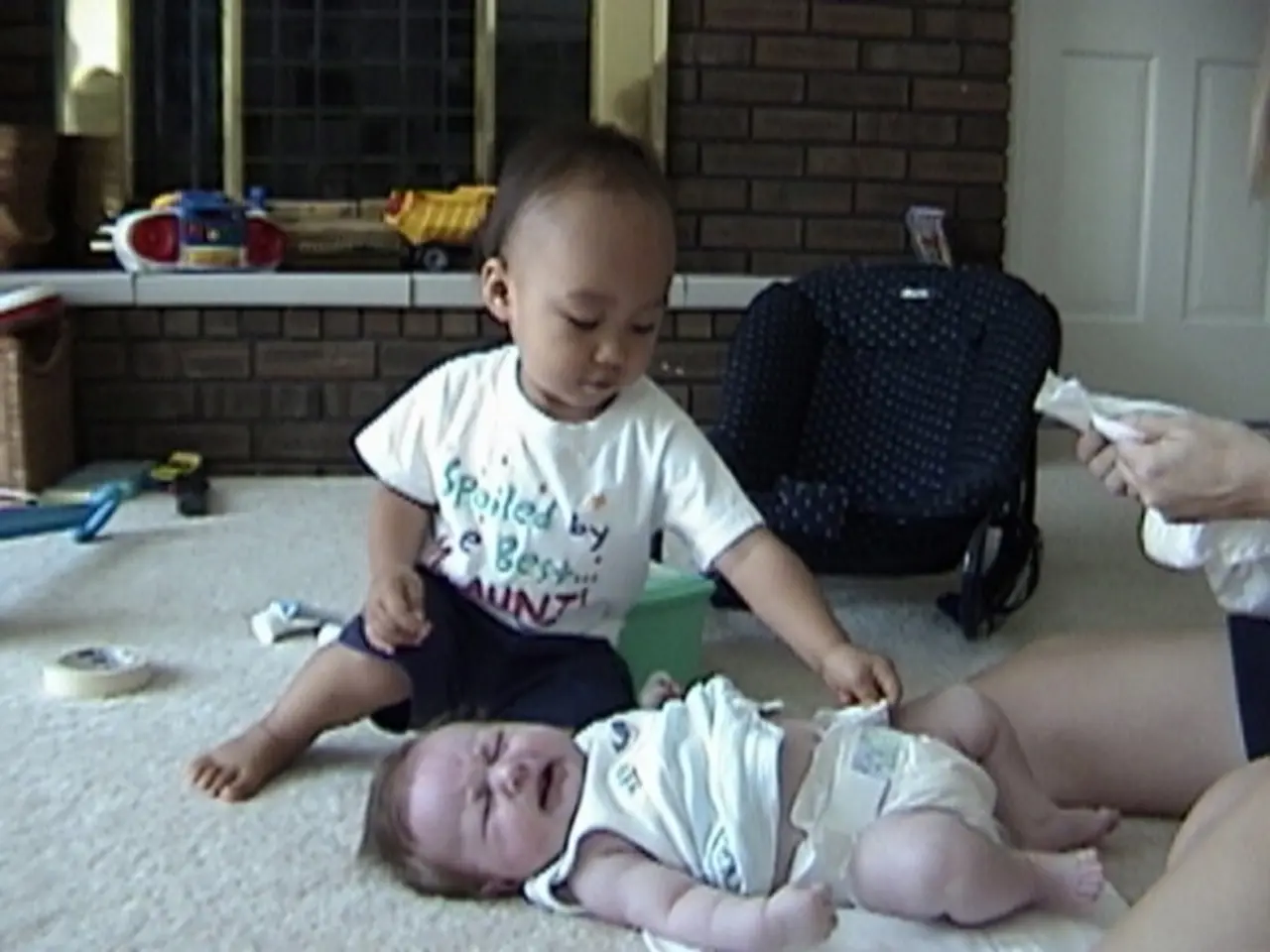
Infants often spit up milk, a condition known as reflux or gastroesophageal reflux (GER). This is relatively normal and not typically a serious issue. When the stomach acid washes back into a baby's food pipe, it's called gastroesophageal reflux. Sometimes, a more severe form called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may occur, causing problems.
The muscle at the end of the food pipe, called the lower esophageal sphincter, usually contracts to prevent stomach contents from flowing back up. In infants under one year, this muscle may not close entirely, causing reflux.
Common causes of GERD in infants include weak LES, food allergies, delayed gastric emptying, premature birth, and neurological or muscular weakness. Understanding these factors can help parents and caregivers address the situation effectively.
GER peaks between 3-4 months of age and tends to decline as the baby matures. However, if symptoms persist and cause feeding refusal, growth issues, irritability, or sleep disturbances, it's crucial to seek advice from a healthcare provider. Other conditions, such as food intolerance, eosinophilic esophagitis, pyloric stenosis, and asthma, can sometimes cause reflux in infants.
Lifestyle changes, such as feeding smaller amounts more frequently, adding thickening agents, and burping the baby regularly, may help improve symptoms for formula-fed babies. In breastfed babies, removing potentially trigger foods from the mother's diet might alleviate symptoms. Laying a baby tummy-side down while awake and after feedings can also reduce reflux episodes.
If medications are unsuccessful and the infant is experiencing severe symptoms or growth issues, surgery may be considered as a last resort. However, most cases of regurgitation or reflux resolve within the first year and require no treatment.
In conclusion, GER is common in infants and typically resolves on its own. Constant vigilance, proper care, and early medical attention, when necessary, can ensure that infants grow and develop without any complications.
- Psoriatic arthritis, an autoimmune disorder that affects the skin and joints, can sometimes occur in individuals with a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Science has been investigating the link between chronic diseases like GERD and cardiovascular health, with some studies suggesting a potential connection.
- Sleep disturbances and issues related to mental health like stress and depression are common among people with chronic diseases like GERD.
- In the realm of health and wellness, taking care of one's digestive health is crucial, as conditions like GERD can impact overall well-being.
- For adults, addressing issues like acid reflux and GERD is an essential part of workplace-wellness programs, as these conditions can affect productivity and quality of life.
- Medication for GERD and other digestive health issues can sometimes lead to side effects like a decreased ability to metabolize certain medications, such as PSA (prostate-specific antigen).
- Medical conditions like GERD, asthma, and other respiratory conditions can affect eye health and require regular eye exams to monitor vision changes.
- Hearing loss and tinnitus, a ringing in the ears, have been associated with long-term use of certain medications used to treat digestive health issues like GERD.
- In the realm of fitness and exercise, maintaining a healthy weight through weight management can help reduce symptoms of digestive health issues like GERD.
- Skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis, have been linked to autoimmune disorders like GERD and require proper skin care and therapies for effective treatment.
- Mental health disorders like depression and anxiety can co-occur with GERD, potentially exacerbating symptoms and requiring a comprehensive approach to treatment.
- Men's health concerns, such as prostate issues and digestive health problems, may benefit from regular screenings and consultations with healthcare providers.
- When considering a healthy lifestyle, making informed choices about nutrition plays a significant role in managing chronic diseases like GERD.
- Aging can lead to a variety of health concerns, including digestive issues like GERD, requiring regular medical check-ups and attention to lifestyle factors.
- Women's health issues extend beyond reproductive health to include conditions like GERD, autoimmune disorders, and mental health concerns, requiring a holistic approach to care.
- Parenting involves staying informed about childhood health issues like GERD, learning about common causes and symptoms to provide optimal care for infants.
- Neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis (MM) and muscular disorders like myasthenia gravis can share symptoms with GERD, requiring a thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals.
- Considering the importance of maintaining overall health and well-being, Medicare plans often provide coverage for healthcare services ranging from GERD treatments to mental health services, helping ensure seniors have access to comprehensive care.